CimTrak for Cloud Security
Security Controls for the Cloud Workload

Cloud Security
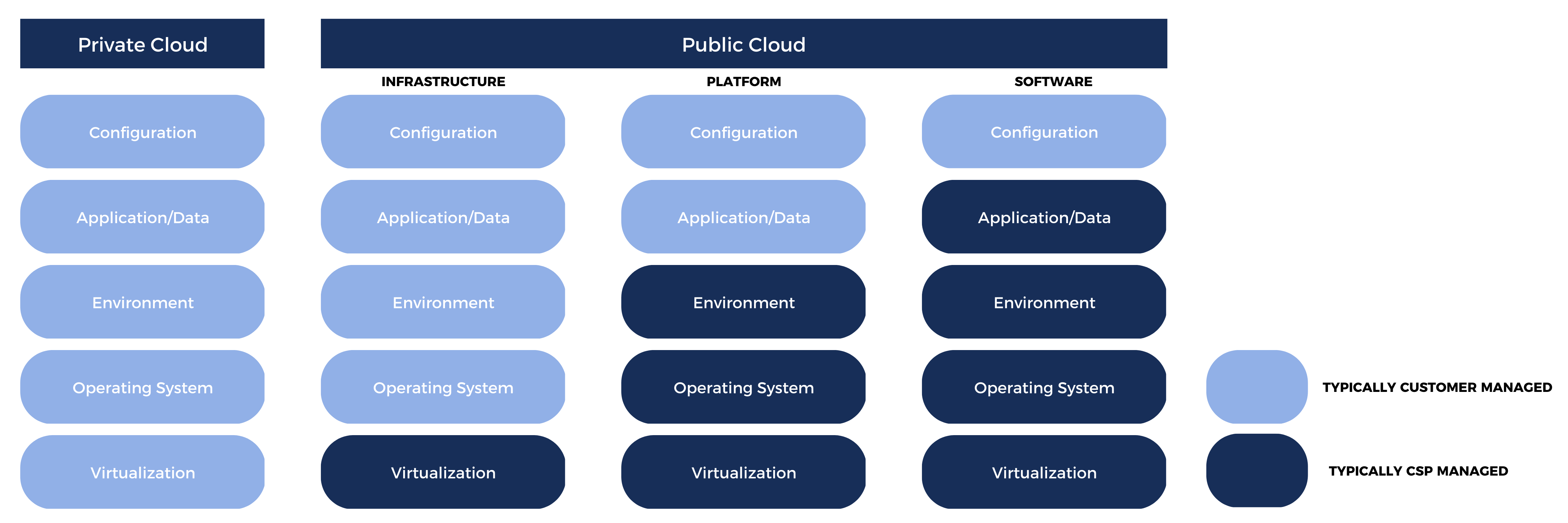
Security in the cloud is a shared responsibility and requires the same knowledge, expertise, and technology as if IT were being delivered via on-prem. Currently, the general concept is that a Cloud Service Provider (CSP) assumes the responsibility "of" the cloud, where customers control the data and configurations "in" the cloud.
Customers are essentially responsible for:
Operating Systems, Network, and Firewall Configurations
Workload/Platform Integrity, Application, and Identity & Access Management
Customer Data and Encryption
While perimeter and signature defenses such as firewalls, intrusion detection, vulnerability assessments, anti-virus, and anti-spam are essential components of your security strategy, they are often defenseless against zero-day exploits, individual attacks, social engineering, and insider exploits.
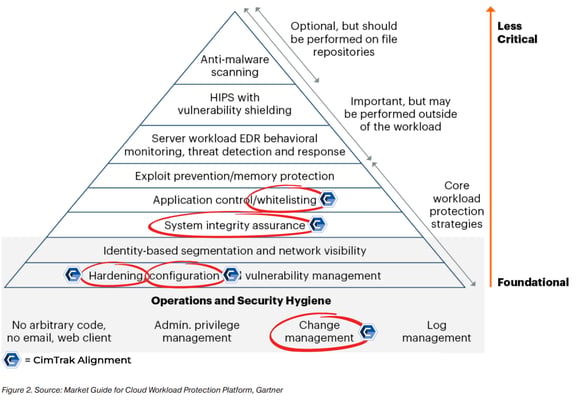
CimTrak is attack-vector independent and provides unprecedented security and compliance capabilities across your organization. CimTrak's real-time detection, automated workflow, and self-healing ability make it one of the most powerful cloud security tools. CimTrak's Integrity Suite aligns with Gartner's Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) and provides five foundational and core features and functionality:
Cloud Security Alliance's (CSA) 2022 annual report outlined the top concerns for threats in cloud computing. Coming in at #3 was misconfiguration and inadequate change control. This is one of the most severe problems relative to a cloud environment, as a misconfiguration can be compounded exponentially given the interconnection of multiple systems and applications.
Key takeaways to mitigate the risk of misconfiguration and inadequate change control as outlined by CSA include:
- Companies need to adopt a technology that can continuously scan for misconfigured assets and remediate those vulnerabilities in real-time.
- Change control must be required to ensure approved changes are made properly and verified through workflow automation.
CimTrak provides...
System/device hardening
Configuration management
Change control
Change reconciliation
Change prevention
Roll-back and remediation
Use of allowlists
Use of file reputation services
Digest STIX & TAXII feeds
Customers are still responsible for the confidentiality and integrity of their IT services, while Cloud Service Providers CSPs assume the role of availability. Gartner’s Cloud Workload Protection Platform is a good illustration of what customers must consider when partnering with a CSP, whether it includes traditional servers, virtual machines, containers, etc...
Moving from on-prem to the cloud is simply moving an asset from one physical location to the next.
Shared responsibility varies by CSP, by cloud service type (Platform as a Service [PaaS] vs. Infrastructure as a Service [IaaS]), and by specific product offering (unmanaged virtual machines vs. managed). A general mapping of roles and responsibilities can be seen in Figure 1.