If a sophisticated hacker targeted your organization tomorrow, how prepared are you to prevent, detect, or recover from that breach?
Without a solid understanding of your current cybersecurity systems, weaknesses, and maturity level, you will struggle to respond to a breach promptly, let alone prevent one altogether. Fortunately, understanding your cybersecurity processes doesn’t have to be complicated. You can achieve this by conducting a cybersecurity posture assessment.
You’ll need to follow five critical steps to
conduct a cybersecurity posture assessment and set your infrastructure up for success. We’ll cover all five steps, then give you tips on maintaining continuous compliance.
What is a Cybersecurity Posture Assessment?
A cybersecurity posture assessment is an evaluation of the resilience of your technical infrastructure and security protocols. It’s used to determine your business's vulnerability to threats like phishing, denial of service, malware, and ransomware.
This type of assessment generally includes a review of technical controls like firewalls and intrusion detection systems, as well as non-technical controls like policies and procedures.
Why Conduct Routine Cybersecurity Posture Assessments?
Regular assessment of your cybersecurity posture is essential because it helps you identify and correct vulnerabilities in your security systems. Assessments help you prioritize risk management efforts and take action on the biggest threats.
It’s important to assess your cybersecurity posture if you are required to comply with regulations like HIPAA, PCI DSS, or ISO 27001. Routine assessments help ensure you take the right actions to remain compliant.
Conducting a Cybersecurity Posture Assessment: The Basics
Before we get into the five steps you can use to conduct your cybersecurity posture assessment, let’s ensure we are on the same page about a few key terms. When discussing cybersecurity posture, we refer to any processes and practices your organization undertakes to prevent cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity posture is vital to assess because this type of assessment allows you to determine the security status of your networks, information, and systems. The ever-changing nature of cybersecurity and cyberattacks means you must regularly conduct assessments to manage your defenses over time and keep your infrastructure secure.
Before beginning your cybersecurity posture assessment, you must first gather some baseline information:
- Business Needs: What are your organization’s current needs? What are your business’s goals for the upcoming quarter or year?
- Current Assets: What hardware and software do employees use within your business? Do you have a BYOD policy that allows employees to use personal devices to access organizational data?
This post will cover five vital steps you must take to conduct a cybersecurity posture assessment:
- Examine Security Controls
- Identify Weaknesses and Attack Vectors
- Map Your Attack Surface
- Select Your Cybersecurity Framework
- Improve Your Cybersecurity Posture
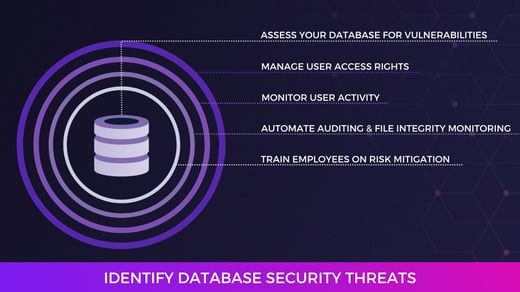
1. Examine Security Controls
Before beginning your assessment, you’ve taken stock of your business’s physical assets and cloud/mobile applications. Your next step is to examine the security controls present on those assets.
Related Read: The 8 Top BYOD Security Risks (and How to Mitigate Them)
What security processes are currently in place in your organization? Some common controls you may have in place include:
- Firewalls
- Automated alerts
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS)
- File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) solutions
Consider how well these controls might protect your organization against hackers and insider threats. For example, a simple File Integrity Monitoring tool might alert your IT team when an unauthorized change is made. Still, if your system is riddled with change noise, you may miss vital alerts, making your monitoring processes less effective than needed to keep your data secure.
2. Identify Weaknesses and Attack Vectors
Your examination of security controls will likely reveal gaps. These gaps are the target of step two of your cybersecurity posture assessment, identifying weaknesses and possible attack vectors.
What is an attack vector? Any weakness an attacker can exploit to breach your network qualifies as an attack vector.
Related Read: Top 5 Network Security Risks and Threats
Some examples include:
- Insufficient cloud security
- Insider threats
- Social engineering and phishing attacks
- DDoS attacks
Understanding the tactics a cybercriminal may use to access your network and exploit or ransom your data is vital to your assessment process. You can use several methods to identify these weaknesses.
First, you can engage in the proactive cybersecurity measure of penetration testing. This type of testing is also sometimes called “ethical hacking.” During a penetration test, a white hat hacker will simulate a cyberattack on your system, probing for weaknesses and vulnerabilities that a true hacker might exploit.
You can also study known risks like existing malware and ransomware. Ensuring your system has adequate protection against these known risks will help to shore up your defenses and improve your cybersecurity posture.
3. Map Your Attack Surface
Step three of your assessment will require you to use the asset inventory you created during your pre-planning process. Combine this information with the attack vectors you identified in the previous step of the assessment.
What assets does your organization own? Explore the potential attack vectors associated with each asset to ensure you are prepared to defend against or respond to a breach. The potential attack vectors of all your combined assets define your organization’s attack surface as a whole.
Related Read: Reviewing the 5 Stages of the Cybersecurity Lifecycle [+ EXAMPLES]
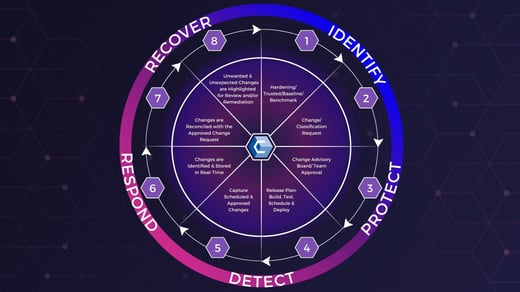
4. Select Your Cybersecurity Framework
Next, you must select a cybersecurity framework, which is a set of guidelines, standards, and best practices for protecting an organization's data. They help provide a structured approach for maintaining effective controls.
Some commonly used cybersecurity frameworks include NIST, ISO 27001, COBIT 5, and PCI DSS.
Your business’s cybersecurity framework will allow you to:
- Identify potential threats
- Implement protections as needed
- Detect threats and breaches
- Respond to a breach in real-time
- Recover in the wake of a cybersecurity incident
5. Improve Your Cybersecurity Posture
Armed with the information gathered in your cybersecurity posture assessment, you are now ready to improve your organization’s cybersecurity processes and procedures. You can improve your cybersecurity posture through several different methods.
Firstly, you may choose to automate certain processes. Automated software updates can ensure you are always operating on the most up-to-date software versions. You may also want to implement a system integrity assurance tool like CimTrak to identify, prohibit, and remediate unauthorized changes in real-time.
Another solution you may want to explore is implementing a Zero Trust Network Architecture. This type of network architecture can improve security and limit the lateral movement of an attacker following a breach. For more information regarding Zero Trust, refer to our post, 6 Top Zero Trust Architecture Benefits and How To Leverage Them.
Additionally, you can conduct regular cyber security training with all staff. Human error accounts for over eighty percent of data breaches. Regular cyber security training can help limit the risk of social engineering attacks and help all staff understand their role in protecting organizational data.
Beyond the Cybersecurity Posture Assessment: Maintaining Continuous System Integrity
Conducting a cybersecurity posture assessment is essential to determining whether your processes, systems, and tools are sufficient to keep your data secure. However, assessments alone aren’t enough to ensure you’re maintaining a secure IT infrastructure.
Continuous file integrity monitoring and system integrity assurance are the best methods for keeping your organization’s sensitive data safe. With proper file integrity monitoring in place, you can detect changes to critical files in real-time, helping you to remediate or even prevent unauthorized changes before they wreak havoc or expose a new vulnerability.
To learn more about the benefits and practices of file integrity monitoring, check out our free resource, the FIM Guide, today!

February 9, 2023